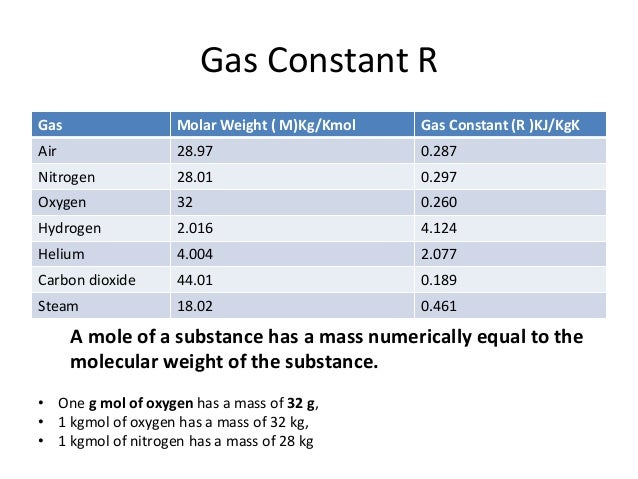
The Universal and Individual Gas Constants in fluid mechanics and thermodynamics. Individual gas constant is given for the most common gases.
Helium He weighs 0.0001785 g/cm³ (0.00010318 oz/in³) weight to volume volume to weight price mole to volume and weight mass and molar concentration density Helium, liquid He weighs 160 kg/m³ (9.98847 lb/ft³) weight to volume volume to weight price mole to volume and weight mass and molar concentration density. Explanation of how to find the molar mass of H2: Hydrogen Gas.A few things to consider when finding the molar mass for H2:- make sure you have the correct ch. Molar mass of Helium = 4 g. The given mass of Helium = 5 2 g. Thus the number of moles of Helium = g i v e n m a s s / m o l a r m a s s.
The Universal and Individual Gas Constants are known from the Ideal Gas Law.
The Individual Gas Constant - R
Molar Mass Of Helium In Kg/mol
The Individual Gas Constant depends on the particular gas and is related to the molecular weight of the gas. The value is independent of temperature. The induvidual gas constant, R, for a gas can be calculated from the universal gas constant, Ru (given in several units below), and the gas molecular weight, Mgas:
R = Ru/Mgas [1]
In the imperial system the most common units for the individual gas constant are ft lb/slug oR. In the SI system the most common units are J/kg K.
Unit conversion: 1 J/kg K = 5.97994 ft lb/slug °R, and 1 ft lb/slug °R = 0.167226 J/kg K.
The Individual Gas Constant for gases:
For full table - rotate the screen!
| Gas | Molecular Weight | Individual Gas Constant - R | |||||||
| Name | Formula | [g/mol], [kg/kmol] | [J/kg K] | [kJ/kg K] | [Wh/(kg K)] | [kcal/(kg K)], [Btu(IT)/lb °F] | [kcal/(lb °F)] | [ft lbf/lb °R] | [ft lbf/slug °R] |
| Acetylene | C2H2 | 26.038 | 319.32 | 0.3193 | 0.08870 | 0.07627 | 0.0623 | 59.350 | 1910 |
| Air | A mixture | 28.9647 | 287.05 | 0.2871 | 0.07974 | 0.06856 | 0.0560 | 53.353 | 1717 |
| Ammonia | NH3 | 17.031 | 488.21 | 0.4882 | 0.13561 | 0.11661 | 0.0952 | 90.740 | 2919 |
| Argon | Ar | 39.948 | 208.13 | 0.2081 | 0.05781 | 0.04971 | 0.0406 | 38.684 | 1245 |
| Butane | C4H10 | 58.122 | 143.05 | 0.1431 | 0.03974 | 0.03417 | 0.0279 | 26.588 | 855 |
| Butene | C4H8 | 56.106 | 148.19 | 0.1482 | 0.04116 | 0.03539 | 0.0289 | 27.543 | 886 |
| Carbon Dioxide | CO2 | 44.010 | 188.92 | 0.1889 | 0.05248 | 0.04512 | 0.0368 | 35.114 | 1130 |
| Carbon Monoxide | CO | 28.010 | 296.84 | 0.2968 | 0.08246 | 0.07090 | 0.0579 | 55.171 | 1775 |
| Carbonic acid | H2CO3 | 62.025 | 134.05 | 0.1341 | 0.03724 | 0.03202 | 0.0261 | 24.915 | 802 |
| Chlorine | Cl2 | 70.906 | 117.26 | 0.1173 | 0.03257 | 0.02801 | 0.0229 | 21.794 | 701 |
| Chloromethane | CH3Cl | 50.488 | 164.68 | 0.1647 | 0.04575 | 0.03933 | 0.0321 | 30.608 | 985 |
| Dichlorofluorumethane | CHCl2F | 102.923 | 80.78 | 0.0808 | 0.02244 | 0.01929 | 0.0158 | 15.015 | 483 |
| Ethane | C2H6 | 30.069 | 276.51 | 0.2765 | 0.07681 | 0.06604 | 0.0539 | 51.393 | 1654 |
| Ethene | C2H4 | 28.053 | 296.38 | 0.2964 | 0.08233 | 0.07079 | 0.0578 | 55.086 | 1772 |
| Fluorine | F2 | 37.997 | 218.82 | 0.2188 | 0.06078 | 0.05226 | 0.0427 | 40.670 | 1309 |
| Helium | He | 4.003 | 2077.1 | 2.0771 | 0.57696 | 0.49610 | 0.4050 | 386.047 | 12421 |
| Hydrogen | H2 | 2.016 | 4124.2 | 4.1242 | 1.14563 | 0.98506 | 0.8043 | 766.541 | 24663 |
| Hydrogen bromide | HBr | 80.912 | 102.76 | 0.1028 | 0.02854 | 0.02454 | 0.0200 | 19.099 | 614 |
| Hydrogen chloride | HCl | 36.461 | 228.04 | 0.2280 | 0.06334 | 0.05447 | 0.0445 | 42.384 | 1364 |
| Hydrogen sulfide | H2S | 34.081 | 243.96 | 0.2440 | 0.06777 | 0.05827 | 0.0476 | 45.344 | 1459 |
| Krypton | Kr | 83.798 | 99.22 | 0.0992 | 0.02756 | 0.02370 | 0.0193 | 18.441 | 593 |
| Methane (natural gas) | CH4 | 16.042 | 518.28 | 0.5183 | 0.14397 | 0.12379 | 0.1011 | 96.329 | 3099 |
| Neon | Ne | 20.180 | 412.02 | 0.4120 | 0.11445 | 0.09841 | 0.0803 | 76.579 | 2464 |
| Nitrogen | N2 | 28.013 | 296.80 | 0.2968 | 0.08245 | 0.07089 | 0.0579 | 55.165 | 1775 |
| Nitrogen dioxide | NO2 | 46.006 | 180.73 | 0.1807 | 0.05020 | 0.04317 | 0.0352 | 33.590 | 1081 |
| Nitrogen trifluoride | NF3 | 71.002 | 117.10 | 0.1171 | 0.03253 | 0.02797 | 0.0228 | 21.765 | 700 |
| Nitrous oxide | N2O | 44.012 | 188.91 | 0.1889 | 0.05248 | 0.04512 | 0.0368 | 35.112 | 1130 |
| Oxygen | O2 | 31.999 | 259.84 | 0.2598 | 0.07218 | 0.06206 | 0.0507 | 48.294 | 1554 |
| Propane | C3H8 | 44.096 | 188.56 | 0.1886 | 0.05238 | 0.04504 | 0.0368 | 35.045 | 1128 |
| Propene | C3H6 | 42.080 | 197.59 | 0.1976 | 0.05489 | 0.04719 | 0.0385 | 36.724 | 1182 |
| Sulfur dioxide | SO2 | 64.064 | 129.78 | 0.1298 | 0.03605 | 0.03100 | 0.0253 | 24.122 | 776 |
| Sulfur hexafluoride | SF6 | 146.055 | 56.93 | 0.0569 | 0.01581 | 0.01360 | 0.0111 | 10.581 | 340 |
| Sulfur trioxide | SO3 | 80.063 | 103.85 | 0.1038 | 0.02885 | 0.02480 | 0.0203 | 19.302 | 621 |
| Water vapor | H2O | 18.015 | 461.52 | 0.4615 | 0.12820 | 0.11023 | 0.0900 | 85.780 | 2760 |
| Xenon | Xe | 131.293 | 63.33 | 0.0633 | 0.01759 | 0.01513 | 0.0123 | 11.770 | 379 |
The Universal Gas Constant - Ru
The Universal Gas Constant - Ru - appears in the ideal gas law and can be expressed as the product between the Individual Gas Constant - R - for the particular gas - and the Molecular Weight - Mgas - for the gas, and is the same for all ideal or perfect gases:
Ru = Mgas R [2]
The Universal Constant defined in Terms of the Boltzmann's Constant
The universal gas constant can be defined in terms of Boltzmann's constant k as:
Ru = k NA [3]
where
k = Boltzmann's constant = 1.381 x 10-23 [J/K]
NA = Avogadro Number = 6.022 x 1023 [1/mol]
The Molecular weight of a Gas Mixture
The average molecular weight of a gas mixture is equal to the sum of the mole fractions of each gas multiplied by the molecular weight of that particular gas:

Mmixture = Σxi*Mi = (x1*M1 + ......+ xn*Mn) [4]
where
xi = mole fractions of each gas
Mi = the molar mass of each gas
The Universal Gas Constant - Ru - in alternative Units
- atm.cm3/(mol.K) : 82.057338
- atm.ft3/(lbmol.K) : 1.31443
- atm.ft3/(lbmol.oR) : 0.73024
- atm.l/(mol.K) : 0.082057338
- bar.cm3/(mol.K) : 83.144598
- bar.l/(mol.K) : 0.083144598
- Btu/(lbmol.oR) : 1.9872036
- cal/(mol.K) : 1.9859
- erg/(mol.K) : 83144598
- hp.h/(lbmol.oR) : 0.0007805
- inHg.ft3/(lbmol.oR) : 21.85
- J/(mol.K) : 8.3144598
- kJ/(kmol.K) : 8.3144598
- J/(kmol.K) : 8314.472
- (kgf/cm2).l/(mol.K) : 0.084784
- kPa.cm3/(mol.K) : 8314.4598
- kWh/(lbmol.oR) : 0.000582
- lbf.ft/(lbmol.oR) : 1545.349
- mmHg.ft3/(lbmol.K) : 999
- mmHg.ft3/(lbmol.oR) : 555
- mmHg.l/(mol.K) : 62.363577
- Pa.m3/(mol.K) : 8.3144598
- psf.ft3/(lbmol.oR) : 1545.3465
- psi.ft3/(lbmol.oR) : 10.73
- Torr.cm3/(mol.K) : 62364
See also:
- More material properties
- The Ideal Gas Law - Gases are highly compressible with changes in density directly related to changes in temperature and pressure.
- A Mixture of Gases - Properties of mixtures of gases.
- More about temperature
Molar Mass Of Helium In Kg/kmol
Related Topics
- Fluid Mechanics - The study of fluids - liquids and gases. Involves velocity, pressure, density and temperature as functions of space and time
- Gases and Compressed Air - Air, LNG, LPG and other common gas properties, pipeline capacities, sizing of relief valves
- Air Psychrometrics - The study of moist and humid air - psychrometric charts, Mollier diagrams, air-condition temperatures and absolute and relative humidity and moisture content
- Material Properties - Material properties for gases, fluids and solids - densities, specific heats, viscosities and more
Related Documents
- Acetone - Thermophysical Properties - Chemical, physical and thermal properties of acetone, also called 2-propanone, dimethyl ketone and pyroacetic acid. Phase diagram included.
- Air - Molecular Weight and Composition - Dry air is a mixture of gases where the average molecular weight (or molar mass) can be calculated by adding the weight of each component
- Air - Thermophysical Properties - Thermal properties of air - density, viscosity, critical temperature and pressure, triple point, enthalpi and entropi, thermal conductivity and diffusicity, and more
- Benzene - Thermophysical properties - Chemical, physical and thermal properties of benzene, also called benzol. Phase diagram included.
- Dry Air Properties - Dry air properties at temperatures ranging 175 - 1900 K - specific heat, ratio of specific heats, dynamic viscosity, thermal conductivity, Prandtl number, density and kinematic viscosity
- Ethylene - Thermophysical Properties - Chemical, physical and thermal properties of ethylene, also called ethene, acetene and olefiant gas. Phase diagram included.
- Gas Mixture Properties - Special care must be taken for gas mixtures when using the ideal gas law, calculating the mass, the individual gas constant or the density
- Gases - Dynamic Viscosity - Absolute viscosities of gases
- Gases - Molar Specific Heat - Molar specific heats of gases at constant volume
- Humid Air and the Ideal Gas Law - Pressure, temperature and volume for an ideal or perfect gas like air with water vapor - or moist air
- Ideal Gas Law - The relations between volume, pressure, temperature and quantity of a gas, including definition of density of a gas
- Mole Fraction of Water Vapor in Moist Air - Mole fraction of water vapor is the ratio of water molecules - to air and water molecules
- Mollier Diagram for Water-Steam - Enthalpy-entropy diagram for water and steam
- Nitrogen - Enthalpy, Internal Energy and Entropy - Enthalpy, internal energy and entropy of Nitrogen as ideal gas
- Non-ideal gas - Van der Waal's Equation and Constants - Listing of van der Waals constants for more than 200 gases, used to correct for non-ideal behavior of gases caused by intermolecular forces and the volume occupied by the gas particles
- Rankine Efficiency - The efficiency of the Rankine cycle
- Ratios of Specific Heat of Gases - Ratios of specific heat for gases in constant pressure and volume processes
- Sulfur Dioxide Liquid - Thermal Properties - Density, specific heat, thermal conductivity and more
- Temperature - Introduction to temperature - including Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin and Rankine definitions - an online temperature converter
- Thermodynamic Terms, Functions and Relations - Common thermodynamic terms and functions - potential energy, kinetic energy, thermal or internal energy, chemical energy, nuclear energy and more
- Total and partial pressure - Dalton's law of partial pressures - How to calculate total pressure and partial pressures for gas mixtures from Ideal Gas Law
Molar Mass Of Helium In Kg
Tag Search
He Element
- en: individual universal gas constant R air helium
